Concept of Networking
Computer networking is the practice of connecting various computing devices, including computers, servers, printers, and smartphones, to enable communication and share resources. These devices can interact over wired connections, like Ethernet cables, or wireless connections, such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, using different protocols. At the heart of computer networking is the transfer of data between devices in packets, which are small pieces of information transmitted across the network. Networking encompasses both hardware components, like routers, switches, and network cables, as well as software protocols, including TCP/IP, DNS, and HTTP, that facilitate seamless data exchange.
The most common types of networks include Local Area Networks (LANs), which are limited to small spaces like homes or offices, and Wide Area Networks (WANs), which span larger regions, such as cities or even entire continents. The internet serves as a massive global WAN that connects millions of devices around the world. Beyond just communication, computer networks facilitate resource sharing, allowing users to access files, printers, and internet services, which boosts collaboration and productivity. Additionally, networks are essential for maintaining security through measures like encryption, firewalls, and secure protocols, protecting data from unauthorized access.
The first operational network, known as ARPANET, was developed in the late 1960s with funding from the U.S. Department of Defense. At that time, government researchers needed a way to share information, as computers were bulky and not easily transportable. Since then, we’ve made significant progress from those early networks. Today, the internet serves as a vast network of networks, linking billions of devices globally. Organizations of all sizes rely on networks to connect their employees’ devices and shared resources like printers.
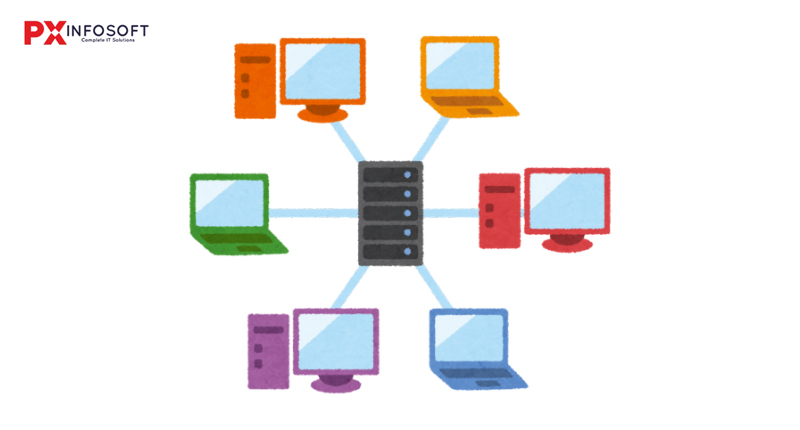
Why use a Computer Network?
In our fast-paced, interconnected world, computer networks play a crucial role in nearly every aspect of our lives—whether we’re surfing the internet, chatting with friends, or working remotely. But what is a computer network, and why is it important? Let’s explore this topic.
A computer network is fundamentally a collection of computers and devices linked together, enabling them to share resources and communicate effectively. You can imagine it as a digital highway, where information, data, and services flow seamlessly from one device to another. Whether it’s a basic home Wi-Fi setup or a large corporate network, the advantages of utilizing a computer network are extensive.
- Efficient Sharing of Resources:- One of the key advantages of using a computer network is the efficient sharing of resources. Without a network, each device—whether it’s a computer, printer, or storage unit—would have to operate independently. However, with a network in place, you can easily share files, printers, internet connections, and even software applications among multiple devices. This not only cuts costs by minimizing the need for numerous physical devices, but it also simplifies everyday tasks. For instance, in a typical office setting, instead of each employee having their own printer, a single shared printer can serve everyone connected to the network. This approach enhances organization and efficiency in both office environments and home setups.
- Better Communication:- When it comes to communication, computer networks play a crucial role. The advent of email, messaging apps, and video conferencing tools such as Zoom and Skype has made it easier than ever to stay connected with people around the world. Whether collaborating with colleagues in different cities or catching up with family, computer networks provide the essential infrastructure for seamless communication. Additionally, social media platforms, online gaming, and collaborative tools like Google Drive depend on computer networks to allow users to connect, share, and interact in real-time. This level of connectivity enhances collaboration, strengthens relationships, and creates opportunities for people to engage in ways that were previously unimaginable.
- Centralized Data Management:- For both businesses and personal use, computer networks allow for centralized data management. Rather than keeping files and documents on separate devices, everything can be stored on a central server or in cloud storage, making it accessible from any device connected to the network. This approach simplifies backup and enhances security, while also ensuring that everyone has access to the latest information. In a workplace setting, centralized data management allows teams to collaborate on projects without the hassle of version control issues, as everyone is working from the same source of truth. For personal use, this means you can access your files, photos, and documents from any device, whether you’re at home, in the office, or on the move.
- Increased Productivity:- With the advantages of resource sharing, improved communication, and centralized data, computer networks inherently enhance productivity. In a business environment, employees can operate more effectively, exchange information instantly, and collaborate across departments without any hold-ups. This increases output and enables organizations to remain competitive. For individuals, a well-functioning home network makes it easy to manage multiple tasks, whether it’s streaming videos, working from home, or tackling personal projects.
- Enhanced Security:- While it may seem that connecting everything to a network raises security concerns, a well-designed network can actually enhance security. By implementing effective firewalls, encryption, and access controls, you can safeguard sensitive information and minimize the chances of data breaches or unauthorized access. In the case of businesses, for instance, sensitive client information and financial records are typically stored on secure networks, which are more closely monitored and controlled than individual devices.
- Scalability:- Computer networks offer scalability. Whether you’re a small business aiming to grow or a family adding more devices to your home network, it’s simple to expand and adjust. Integrating new devices or users into a network can usually be done with minimal effort, making sure that as your requirements grow, your network can adapt accordingly.
Computer networks play a crucial role in enhancing our work, communication, and information management. Whether for personal or business purposes, they enable us to stay connected, share resources, and boost efficiency. Without these networks, many aspects of our daily lives—from remote work to staying in touch with family and friends—would be unfeasible. Therefore, if you haven’t yet embraced a computer network, it may be worth exploring how it can improve your digital experience and connectivity.
Types of Computer Networks
A computer network consists of a group of computers connected through a common communication pathway, enabling them to share resources with one another, which are provided by or situated on the network nodes.
1.Personal Area Network (PAN):- A Personal Area Network (PAN) is a compact network, usually covering a distance of just a few meters, intended for personal devices. It’s the type of network you would typically use at home or while traveling. A personal area network, or PAN, is a compact network centered around an individual or a single device. It connects a limited number of devices within a small, localized space. Instead of incorporating numerous devices, PANs typically function from one or two primary devices. For instance, when you use Bluetooth on your smartphone to share a photo with a nearby device, you’re utilizing a PAN. Its transmission speed is very high with very easy maintenance and very low cost. This uses Bluetooth, IrDa, and Zigbee as technology. Examples of PAN are USB, computer, phone, tablet, printer, PDA, etc.

-
-
- Common Examples
- Connecting your smartphone to a Bluetooth headset or wireless speakers.
- Linking your laptop to your phone via a hotspot.
- Using a Wi-Fi connection to link your laptop and printer.
- Range:- Usually covers a very short distance (around 10 meters or 30 feet).
- Devices:- Smartphones, laptops, tablets, wireless speakers, and smartwatches.
- Types of PAN
- Wireless Personal Area Networks: Wireless Personal Area Networks are created by simply utilising wireless technologies such as WiFi and Bluetooth. It is a low-range network.
- Wired Personal Area Network: A wired personal area network is constructed using a USB.
- Advantages of PAN
- PAN is relatively flexible and provides high efficiency for short network ranges.
- It needs easy setup and relatively low cost.
- It does not require frequent installations and maintenance
- It is easy and portable.
- Needs fewer technical skills to use.
- Disadvantages of PAN
- Low network coverage area/range.
- Limited to relatively low data rates.
- Devices are not compatible with each other.
- Inbuilt WPAN devices are a little bit costly.
- Applications of PAN
-
- Home and Offices
- Organizations and the Business sector
- Medical and Hospital
- School and College Education
- Military and Defense
-
- Common Examples
-
2. Local Area Network (LAN):- A Local Area Network (LAN) is a type of network that links devices within a limited geographical area, such as a home, office, or school. It enables devices to share files, printers, and internet connections. A LAN, or Local Area Network, is the most commonly used type of network. It connects computers through a shared communication path within a limited area, such as a home, school, or office. A LAN typically includes two or more computers linked via a server. The key technologies that enable this network are Ethernet and Wi-Fi. It can cover distances of up to 2 kilometers, offering high transmission speeds, easy maintenance, and low costs. Examples of LANs include networking in homes, schools, libraries, laboratories, and offices.
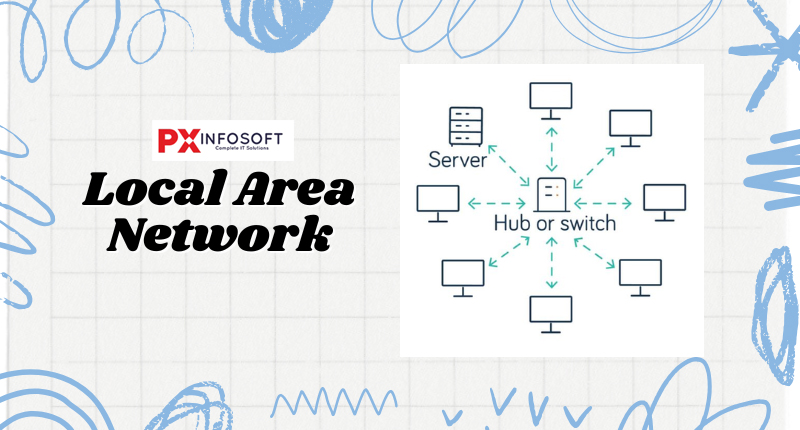
-
- Common Examples
- The Wi-Fi network in your home.
- The network inside an office that connects all computers together.
- Range:- Typically covers a small area like a building or a campus (up to a few kilometers(2 kilometers)).
- Devices:- Computers, printers, routers, switches, and other network devices.
- Advantages of a LAN
- Privacy: LAN is a private network, thus no outside regulatory body controls it, giving it a privacy.
- High Speed: LAN offers a much higher speed(around 100 mbps) and data transfer rate comparatively to WAN.
- Supports different transmission mediums: LAN support a variety of communications transmission medium such as an Ethernet cable (thin cable, thick cable, and twisted pair), fiber and wireless transmission.
- Inexpensive and Simple: A LAN usually has low cost, installation, expansion and maintenance and LAN installation is relatively easy to use, good scalability.
- Disadvantages of LAN
- The initial setup costs of installing Local Area Networks is high because there is special software required to make a server.
- Communication devices like an ethernet cable, switches, hubs, routers, cables are costly.
- LAN administrator can see and check personal data files as well as Internet history of each and every LAN user. Hence, the privacy of the users are violated.
- LANs are restricted in size and cover only a limited area.
- Since all the data is stored in a single server computer, if it can be accessed by an unauthorized user, can cause a serious data security threat.
- Application of LAN
- A variety of devices can connect to LANs, including servers, desktop computers, laptops, printers, IoT devices, and even game consoles.
- In offices, LANs are often used to provide shared access to internal employees to connected printers or servers.
- Common Examples
3. Campus area network (CAN)
A Campus Area Network (CAN) is larger than a Local Area Network (LAN) but smaller than a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN). This type of computer network is typically found in environments such as schools and colleges. While each department in a school might use its own LAN, all the school’s LANs could connect through a CAN. Campus area networks combine several independent networks into one cohesive unit. For example, the English and engineering departments at a university might connect through a CAN to communicate with each other directly. It spans a limited geographical area, often covering multiple buildings within a campus. CAN primarily utilizes Ethernet technology, with a range of 1 to 5 kilometers. It offers high transmission speeds along with moderate maintenance and operational costs. Examples of CAN include networks that serve schools, colleges, and various buildings.
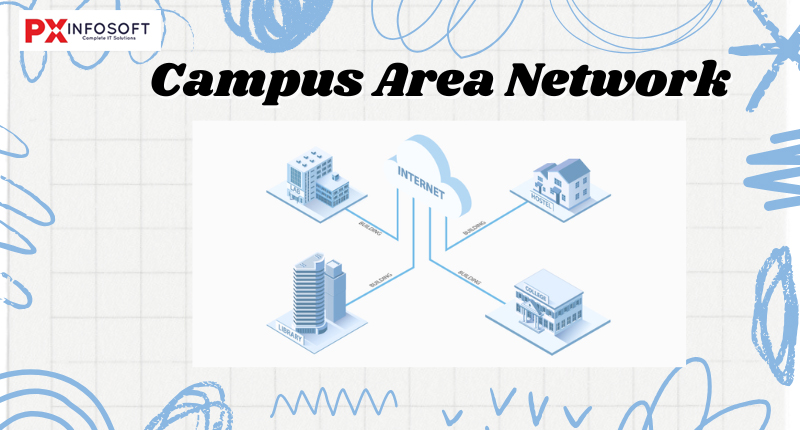
- Common Examples:- A university campus is an excellent example of where a Campus Area Network thrives. With various buildings, such as libraries, laboratories, student centers, and dormitories, a reliable and secure network connection is essential.
- Range:- The range of CAN is 1 km to 5 km. If two buildings have the same domain and they are connected with a network, then it will be considered as CAN only. Though the CAN is mainly used for corporate campuses so the link will be high speed.
- Devices:-
- Networking Hardware: Routers, switches, and firewalls that manage data traffic.
- Connectivity Medium: Ethernet cables, fiber optics, or wireless connections.
- Access Points: Strategically placed to ensure wide coverage.
- Advantages of CAN
- Speed: Communication within a CAN takes place over Local Area Network (LAN) so data transfer rate between systems is little bit fast than Internet.
- Security: Network administrators of campus take care of network by continuous monitoring, tracking and limiting access. To protect network from unauthorized access firewall is placed between network and internet.
- Cost effective: With a little effort and maintenance, network works well by providing fast data transfer rate with multi-departmental network access. It can be enabled wirelessly, where wiring and cabling costs can be managed. So to work with in a campus using CAN is cost-effective in view of performance
- Disadvantages of CAN
- Complex implementation, management, and design.
- Increased cybersecurity challenges, especially in large networks.
- Requires ongoing maintenance and administration.
- Potential single points of failure.
- Relies on physical infrastructure.
- Application of CAN :- Campus networks are used in manufacturing, warehousing, universities, and also in corporate and industrial settings. Campus Area Networks (CAN) provide more control over network resources and typically relies on a centralized hub to which other locations connect, when compared to public networks.
4. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A metropolitan area network, or MAN, is a medium-sized network that is larger than a campus area network (CAN). Although a MAN can be expensive to set up, it offers effective connectivity between devices over a broad geographical area. For instance, a city government might utilize a MAN to connect its various offices spread throughout the metropolitan region. This network mainly uses FDDI, CDDI, and ATM as the technology with a range from 5km to 50km. Its transmission speed is average. It is difficult to maintain and it comes with a high cost. Examples of MAN are networking in towns, cities, a single large city, a large area within multiple buildings, etc.
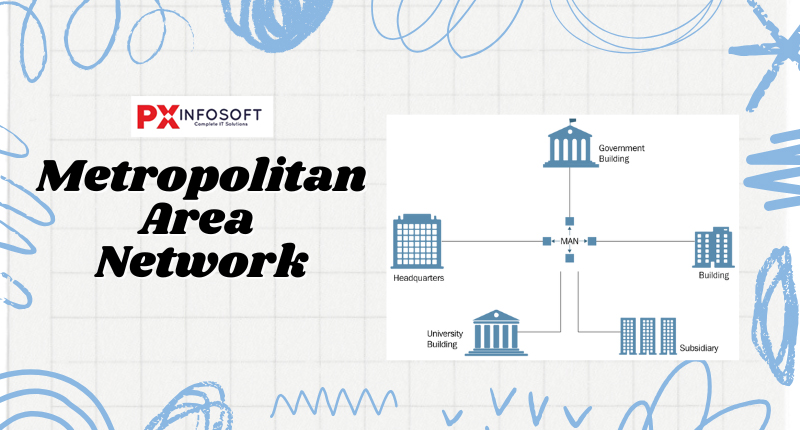
- Common Examples
- A city’s network that links different local schools, libraries, or government buildings.
- Internet service providers connecting large buildings within a metropolitan area.
- Range:- Covers a city or a large campus (typically from 5 to 50 kilometers).
- Devices
- Routers
- Fiber-optic cables
- Switches
- High-speed internet connections
- Advantages of MAN
- MAN offers high-speed connectivity in which the speed ranges from 10-100 Mbps.
- The security level in MAN is high and strict as compared to WAN.
- It support to transmit data in both directions concurrently because of dual bus architecture.
- MAN can serve multiple users at a time with the same high-speed internet to all the users.
- MAN allows for centralized management and control of the network, making it easier to monitor and manage network resources and security.
- Disadvantages of MAN
- The architecture of MAN is quite complicated hence, it is hard to design and maintain.
- This network is highly expensive because it required the high cost to set up fiber optics.
- It provides less fault tolerance.
- The Data transfer rate in MAN is low when compare to LANs.
- Application of MAN:- MANs are used to connect different buildings within a university, ensuring high-speed data transmission across campuses. Used for large-scale data gathering and analysis in urban planning and environmental studies.
5. Wide Area Network (WAN)
A WAN, or Wide Area Network, is a type of computer network that links computers across large geographical distances using a shared communication path. Unlike local networks, it spans multiple locations. A WAN can also be described as a collection of local area networks (LANs) that connect with each other over distances greater than 50 kilometers. Technologies such as leased lines and dial-up are commonly used for WAN connections. However, the transmission speeds tend to be quite low, and the maintenance costs are typically very high. The most well-known example of a WAN is the Internet.
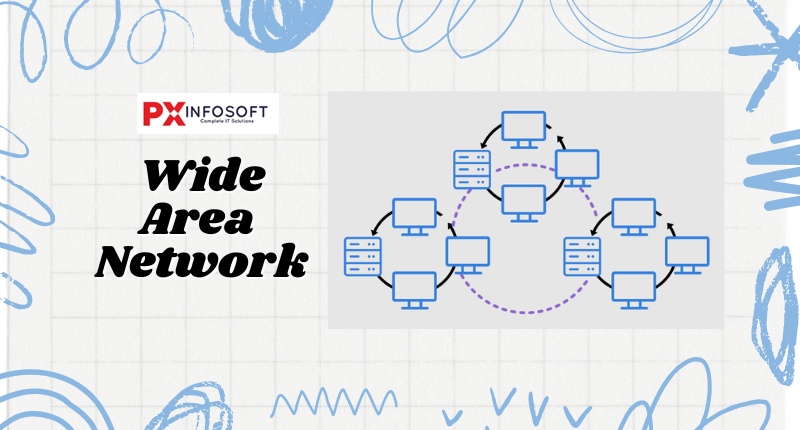
- Common Examples
- Connecting remote office branches of a company across different countries.
- The global internet infrastructure connecting people worldwide.
- Range:- Covers a vast area, often worldwide.
- Devices
- Routers,
- Satellites
- Fiber-optic cables
- Long-distance transmission systems.
- Advantages of WAN
- Covers a broader geographic area.
- It benefits the global market and business.
- IT infrastructure is centralized.
- Increase your privacy.
- Assists global markets and businesses.
- Allows users to share resources and application software.
- Disadvantages of WAN
- It is very expensive because we must pay each time we transfer data.
- Troubleshooting WAN can be time-consuming and challenging.
- Wide Area Network is insecure and untrustworthy.
- Because it is a public network, it is heavily reliant on a third party.
- Application of WAN :- A WAN serves as a network of networks, enabling connectivity across long distances. This supports essential functions for organizations, such as sharing resources, exchanging data, and accessing centralized applications for branches located in different geographical areas.
6. Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
A wireless local area network, or WLAN, functions much like a LAN by transmitting data over a limited area. Devices using a WLAN usually don’t require a wired connection. Although it tends to be less secure and somewhat weaker than other types of networks, a WLAN offers users the convenience of using their devices in different locations. A Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) functions similarly to a traditional LAN, but it connects devices using radio waves (Wi-Fi) rather than physical cables. This technology is widely used in homes, offices, and public spaces such as cafes.
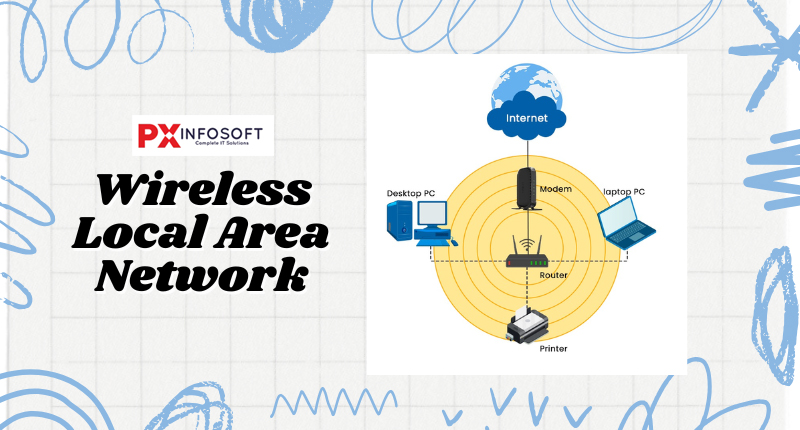
- Common Examples
- Your home’s Wi-Fi network.
- The Wi-Fi at a coffee shop or library.
- Range:- Typically ranges from 30 meters to 100 meters indoors (depending on the router).
- Devices
- Laptops
- Smartphones
- Tablets
- Routers
- Access points.
- Advantages of WLAN:- WLANs are easier to install and manage. They require less physical equipment compared to wired networks, which saves you money, cuts down on installation time, and takes up less space in an office environment.
- Disadvantages of WLAN:- WLANs can face bandwidth limitations because the wireless medium is shared, leading to slower speeds. Additionally, WLANs are susceptible to interference from other wireless devices, which can cause performance issues or dropped connections.
- Application of WLAN :- In office environments, a Wireless LAN network enables employees to connect their devices to the internet and share resources like printers and files with one another. Additionally, the Wireless LAN network provides customers with internet access in public spaces, such as coffee shops.
7. Storage Area Network (SAN)
A storage area network, commonly known as a SAN, is a specialized network designed for teams to store large volumes of sensitive data. It allows for the centralization of data on a separate network, distinct from the primary operating network. For instance, a SAN might be used by your team to keep customer information on a different network, ensuring that the main network maintains its high speeds.
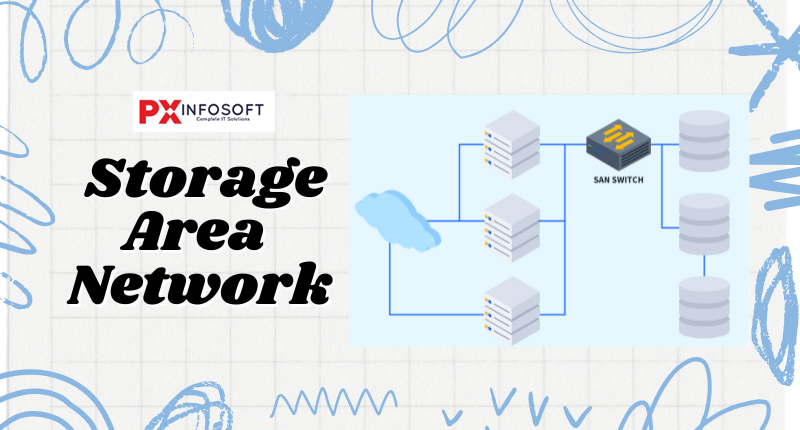
- Common Examples
- Large businesses storing and managing huge amounts of data across multiple servers.
- Data backup systems for enterprises.
- Range:- The range depends on the organization and how it’s structured. It could span multiple buildings in a campus.
- Devices
- Storage devices
- Servers
- Switches
- Storage management systems.
- Advantages of Storage Area Network:- A SAN removes the conventional dedicated link between a network file server and storage, along with the idea that the server controls and manages the storage devices. This change helps to eliminate bandwidth bottlenecks. Additionally, a SAN addresses single points of failure, improving the reliability and availability of storage.
- Disadvantages of Storage Area Network:- Expensive & Long-term Return on Investments (ROIs) – SAN systems are designed for large-scale deployments and high-performance workloads. As a result, they are generally more costly than other storage types, such as file and object storage, and the returns on investment tend to increase gradually over time.
- Application of Storage Area Network
- Databases and database management systems.
- Server virtualization.
- Business applications.
- Virtual desktop infrastructure.
- Development and testing.
8. Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A virtual private network, or VPN, is a private network that operates over the internet. It works similarly to an EPN by offering a secure and private connection. However, VPNs usually don’t need the same infrastructure as EPNs. Both individuals and businesses can utilize VPNs to maintain their privacy and security.

- Common Examples
- Accessing your work network remotely when traveling.
- Using a VPN service to browse the internet securely or to bypass geographic restrictions (like watching content from a different country).
- Range:- The “range” isn’t a physical distance; it links users through the internet, no matter where they are located.
- Devices
- Computers
- Smartphones
- Routers
- VPN servers.
- Advantages of Virtual Private Network
- Ensure your network is secure.
- Protect your personal information.
- Stop data throttling.
- Eliminate bandwidth throttling.
- Gain access to geo-restricted services.
- Enhance network scalability.
- Lower support expenses.
- Disadvantages of Virtual Private Network
- Reduced Internet Speed.
- Cost Considerations.
- Complex Setup and Configuration.
- Blocked Access to Certain Websites.
- Security Concerns: Not All VPNs Are Created Equal.
- Dependency on Service Reliability.
- Legal and Policy Restrictions.
- Logging Policies: Potential Privacy Concerns.
- Application of Virtual Private Network:- A VPN, or virtual private network, creates a secure digital connection between your computer and a remote server operated by a VPN provider. This connection forms a point-to-point tunnel that encrypts your personal data, hides your IP address, and allows you to bypass website restrictions and firewalls on the internet.
9. Client-Server Network
Client-server networks are systems where a dedicated computer stores data, manages resources, and controls user access, known as the server. This server acts as a hub, connecting all other computers in the network. Any machine that connects to the server is referred to as a client. In this setup, the server is a robust computer that offers resources such as files, printers, or services to the clients, which depend on the server to access these centralized resources.
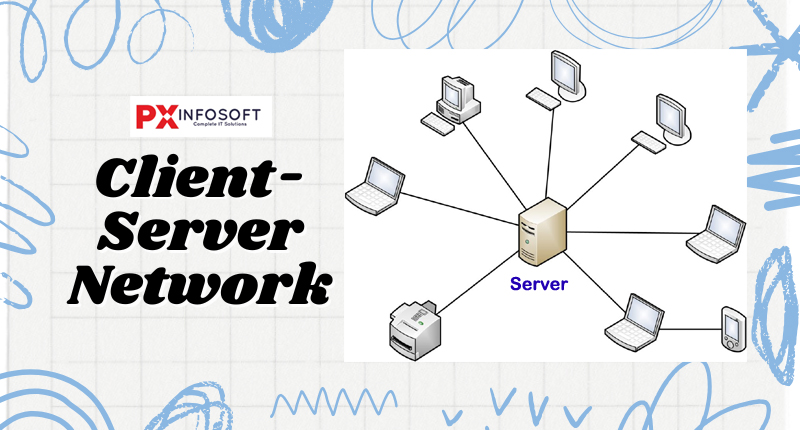
- Common Examples
- Email servers where the server stores and manages email messages, and clients access them.
- Websites that are hosted on servers and accessed by users via browsers.
- Range:- The range depends on the type of network; it could be LAN, WAN, or even the internet.
- Devices
- Servers
- Client computers
- Networking equipment.
- Advantages of Client-Server Network
- Less damage occurs because one client computer does not affect the others in the network.
- File recovery is straightforward since backups are managed centrally by network administrators.
- It is more secure as files and all other data are centralized within these networks.
- Disadvantages of Client-Server Network:- One major drawback of a client-server model is the risk of system overload due to insufficient resources to accommodate all clients. When too many clients attempt to connect to the shared network simultaneously, it can lead to connection failures or slowdowns.
- Application of Client-Server Network:- A client-server network is set up for end-users, known as clients, to access resources like files, music, video collections, or other services from a central computer referred to as a server. The primary role of a server is to fulfill its name’s purpose – to serve its clients!
10. Peer-to-Peer Network (P2P)
A peer-to-peer (P2P) network consists of a group of computers that operate as equal nodes for sharing files. Rather than relying on a centralized server to act as a shared drive, each computer serves as its own server for the files it holds. In a P2P network, every computer (or peer) functions both as a client and a server. This setup allows devices to share resources directly with one another, eliminating the need for a central server.

- Common Examples
- File-sharing networks like BitTorrent.
- Sharing files between two or more computers directly, without the need for a central server.
- Range:- Can be small (in a home) or large (in a decentralized global network like some file-sharing platforms).
- Devices
- Computers
- Laptops or mobile devices acting as both clients and servers.
- Advantages of Peer-to-Peer Network:- The main advantage of a peer-to-peer network is its simplicity in setup. In these networks, all nodes function as both servers and clients, eliminating the need for a dedicated server. Additionally, peer-to-peer networks tend to be more cost-effective.
- Disadvantages of Peer-to-Peer Network
- A computer can be accessed at any time.
- Network security needs to be implemented on each computer individually.
- Backups must be done for each computer separately.
- There is no centralized server to manage and control data access.
- Application of Peer-to-Peer Network:- P2P technology is utilized in instant messaging applications. For example, apps like Skype and WhatsApp leverage P2P communication, allowing users to chat and make voice and video calls directly with one another. This means that messages and media files are shared between users without the need for a central server.
11. Cloud Network
Cloud networking refers to the virtual components, topologies, and configurations of networks that operate on a cloud provider’s physical infrastructure. You have the ability to define and manage your networks through software. This allows you to create your own virtual local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs) using cloud resources. A Cloud Network connects users to virtual resources available on the internet, rather than relying on physical hardware. This type of network is commonly utilized for online storage, software-as-a-service (SaaS), and various other cloud computing services.

- Common Examples
- Google Drive, Dropbox, or iCloud for cloud storage.
- Online applications like Google Docs or Microsoft 365.
- Range:- Can be accessed from anywhere as long as you have an internet connection.
- Devices
- Computers
- Smartphones
- Tablets
- Cloud servers
- Internet infrastructure
- Advantages of Cloud Network
- Faster time to market. You can quickly create or shut down new instances in seconds
- Enabling developers to speed up their work with rapid deployments.
- Scalability and flexibility.
- Cost savings.
- Improved collaboration.
- Enhanced security.
- Data loss prevention.
- Disadvantages of Cloud Network
- Data loss or theft.
- Data leakage.
- Account or service hijacking.
- Insecure interfaces and APIs.
- Denial of service attacks.
- Technology vulnerabilities, particularly in shared environments.
- Application of Cloud Network
- Cloud Storage Services.
- Office Productivity Suites.
- Video Conferencing Platforms.
- Cloud-Based Development Environments.
- Cloud Backup Solutions.
- Cloud-Based Social Media Platform1.
- Cloud-Based Accounting Applications.
- Cloud-Based Gaming Services.
Other Types of Computer Networks
- Passive Optical Local Area Network (POLAN):- A POLAN is a type of computer network that serves as an alternative to a LAN. It utilizes optical splitters to divide an optical signal from a single strand of single-mode optical fiber into multiple signals, allowing for the distribution of users and devices. Essentially, POLAN represents a point-to-multipoint LAN architecture. A passive optical local area network, or POLAN, is a cost-effective solution that can connect various locations to a central network. POLANs are capable of linking multiple entities to a single hub of information. For instance, if a school district’s headquarters needs to connect with each school in its district, it might choose to implement a POLAN.
- Enterprise private network (EPN):- An enterprise private network (EPN) is a specialized computer network primarily utilized by businesses seeking a secure connection across multiple locations to share resources. This exclusive network is designed and managed by the company itself, allowing for high-speed sharing of company assets. EPNs are generally tailored to the specific needs of a single organization, which enhances security. For instance, a technology firm with high-security requirements may implement an EPN to minimize the chances of data breaches.
- Home Area Network (HAN):- Many homes may have multiple computers. To connect these computers and other peripheral devices, a network should be set up, similar to a local area network (LAN) within the house. This type of network, which enables users to link several computers and digital devices in the home, is known as a Home Area Network (HAN). HAN facilitates the sharing of resources, files, and programs among devices on the network and supports both wired and wireless communication.
- System-area network (SAN):- A system area network, or SAN, is an extensive local network that facilitates connections within clusters. The different devices linked to a SAN function as a unified system. SANs are emerging networks that operate at high speeds.
Summary of Key Differences
| Type of Network | Coverage Area | Example Use Case | Main Devices Used |
| PAN | Small (within a person’s reach) | Connecting personal devices (e.g., Bluetooth headsets) | Smartphones, tablets, laptops |
| LAN | Small area (home or office) | Home or office network | Computers, printers, routers |
| MAN | City or campus-wide | City-wide network, campus network | Routers, fiber-optic cables |
| WAN | Wide, global range | The internet, connecting remote offices | Routers, satellites, servers |
| WLAN | Smaller area (within a building) | Wireless internet access in homes or public places | Wi-Fi routers, access points |
| SAN | Localized (business/data centers) | Centralized data storage in companies | Storage devices, servers, switches |
| VPN | Global (over the internet) | Secure remote access to private networks | VPN servers, computers, routers |
| Client-Server | Varies (depends on network setup) | Web hosting, email servers | Servers, client computers |
| P2P | Small to large (depends on the network) | File sharing between devices | Computers, smartphones |
| Cloud | Anywhere with internet access | Online storage, SaaS applications | Computers, tablets, servers |
Conclusion
In conclusion, computer networks play a crucial role in linking different computer devices to facilitate the efficient sharing of data and resources. Networks such as PAN, LAN, CAN, MAN, and WAN cater to diverse applications and needs, each offering unique benefits and limitations. Gaining insight into these networks and their uses enhances connectivity, data transfer, and resource management across a spectrum of scenarios, from personal use to global communications.